Q: During extended periods of fasting, the body shifts from using glucose as its primary fuel source to producing molecules from fat stores. What are these molecules called, which provide an alternative energy source for the brain and muscles?
A: Ketones
Q: When fasting, the body triggers the release of a specific hormone produced in the stomach that signals hunger and stimulates the release of growth hormone. Paradoxically, this hormone also plays a role in maintaining insulin sensitivity. What is the name of this hormone?
A: Ghrelin
Q: Fasting involves the activation of a group of proteins often linked to lifespan extension and disease prevention. _____ is the name of these longevity-related proteins activated by fasting.
A: Sirtuins
Q: Human survival has been shaped by periods of food scarcity, driving the evolution of metabolic adaptations that allowed ancient humans to thrive in fasting conditions. This concept suggests that the ability to store fat efficiently may have once provided an evolutionary advantage. What is the name of this evolutionary theory?
A: Thrifty gene hypothesis
Q: _____ is a metabolic condition, often improved by fasting, characterised by high blood sugar and insulin resistance.
A: Type 2 Diabetes
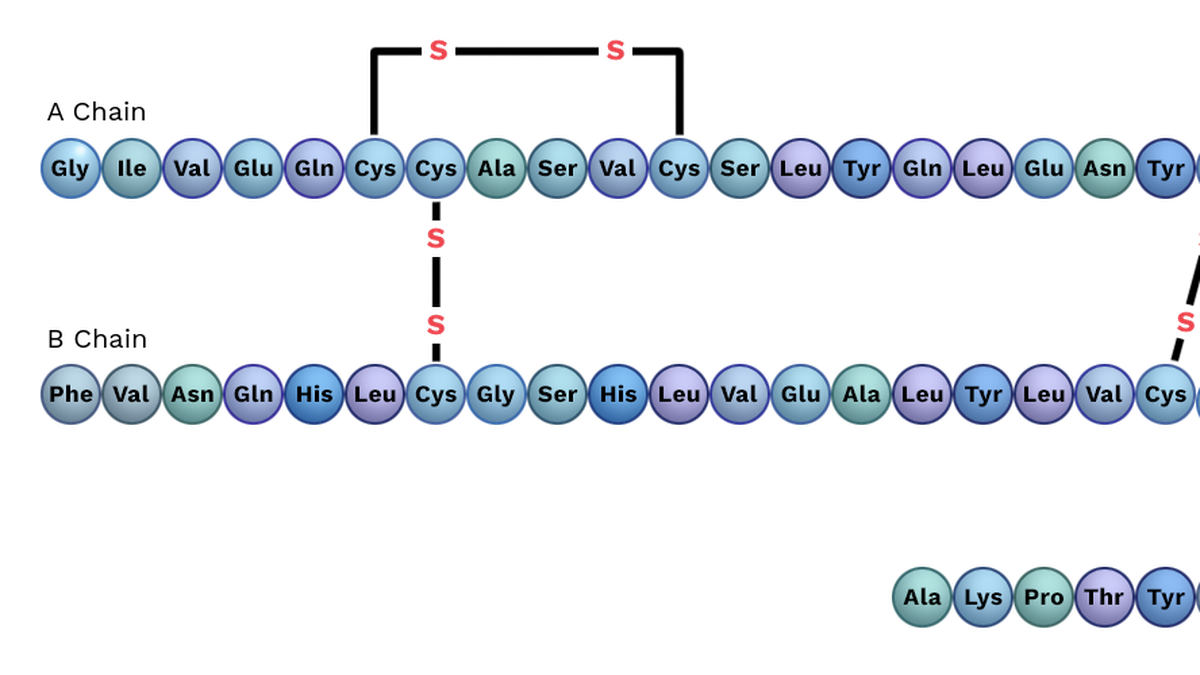
Q: Visual question: Identify the structure of the hormone shown in the image that is secreted by the pancreas and regulates blood sugar levels, which decreases during fasting and allows fat cells to release stored energy.
A: Insulin
Published – October 04, 2024 11:21 am IST