The World Health Organisation (WHO) on August 14, 2024, declared the mpox outbreak as a “global health emergency”
The mpox or monkeypox outbreak has affected over 115 countries, and is the worst in the Democratic Republic of Congo and neighbouring countries.
The outbreak first started in 2022. The WHO decided to change the name of monkeypox to mpox in November of that year following racist insinuations towards some communities
According to data collected from national authorities, 99,176 cases of mpox were confirmed between January 1, 2022 and June 30, 2024, and 208 people died.
What is this virus?
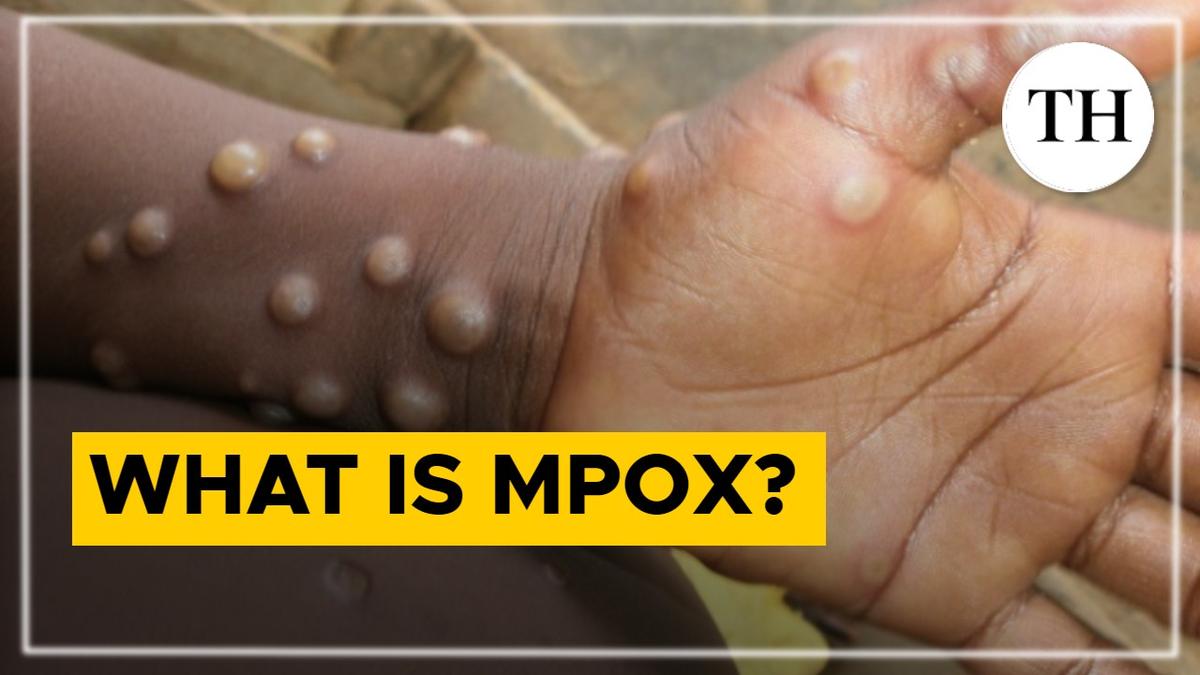
The monkeypox virus is an orthopoxvirus, which is a genus of viruses that also includes the variola virus, which causes smallpox.
Monkeypox is a zoonosis, a disease that is transmitted from infected animals to humans.
According to the WHO, cases occur close to tropical rainforests inhabited by animals that carry the virus. Monkeypox virus infection has been detected in squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and some species of monkeys.
Human-to-human transmission of the virus is, however, limited. It can be through contact with bodily fluids, lesions on the skin, the respiratory tract or through the eyes, nose or mouth or by virus-contaminated objects, such as bedding and clothing.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or CDC, the infection was first discovered in 1958. Two outbreaks of a pox-like disease were recorded in colonies of monkeys kept for research — which led to the name ‘monkeypox’.